| Date :03-May-2019 |
Staff Reporter:
IN RESPONSE to‘The Hitavada’ campaign for trees, individuals, social and non-governmental organisations have started coming forward in support. It has evoked response not only from Nagpurians but also from sensitive institutions like ‘Integrated Design, Landscape Architect’ of Bengaluru. In order to make the public, developers and authorities aware of damages caused to trees due to development activities and measures to be taken for protecting trees, the institution has come up with a compilation with the help of graphics. Paramjit Singh Ahuja, a c c l a i m e d Architect and envir o n m e n t a l i s t , shared the compilation with ‘The Hitavada’ and extended support to the ongoing campaign.
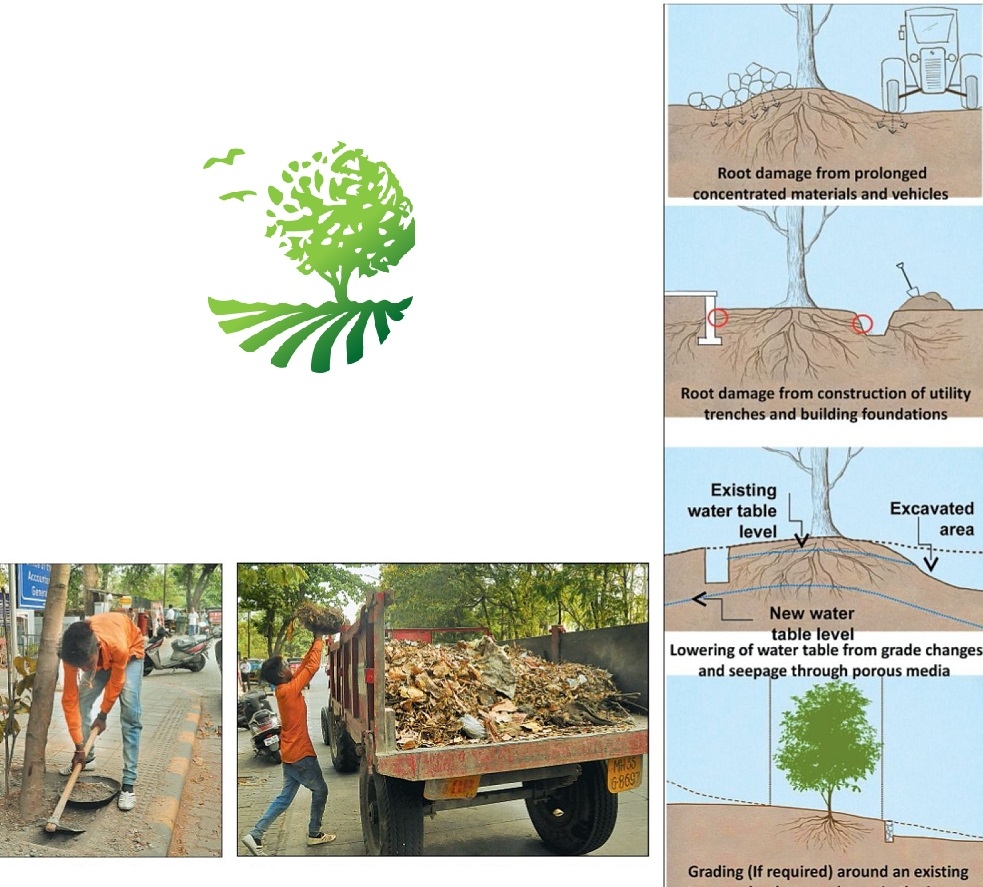
Ahuja said, “The Hitavada has been carrying out a campaign for preservation of trees, which have become a casualty in the wake of development activities. The process involved with development activities can be deadly to trees. Unless the damage is extreme, the trees may not die immediately but could decline over years. ...And therein lies the rub because the slow but eventual death of the tree is not recognisable as being associated with development activity, which in the first place is responsible for its death.” Following the campaign, the civic authorities have initiated a programme of de-choking of trees. Still, the engineers are not aware about the process of dechoking of trees, measures to be taken to protect them.
With better awareness, the death of trees on account of development activities is preventable. According to Bengaluru-based ‘Integrated Design, Landscape Architect’, the access should be in limit when the development work is underway. If at all possible, it is best to allow only one access route on and off the property. All contractors must be instructed where they are permitted to drive and park their vehicles. Often this same access drive can later serve as the route for utility wires, water lines, or the driveway. Storage areas for equipment, soil, and construction materials should be specified before the commencement of construction work.
The areas for burning (if permitted),cement wash-out pits, and construction work zones should be limited and away from protected trees. The organisation cautioned about compaction of soil and suggested that its hould be avoided as this destroyed the soil pore structure which altered water up take abilityof tree.Compaction is causedby storage of materials, machinery and soil and by the use of an area as thoroughfare by people and vehicles.Hence,storage of material should be done at a specified area away from the protected zone of the trees. Change in the existing ground levels can also affect the trees. Reduction in ground level causes the severance of roots, whereas increase in ground level causes compaction and can suffocate and damage shallow and fragile roots. Hence, the existing ground levels should not be changed, pointed out the organisation. It has suggested reduction of impact due to machinery. According to the organisation, impact due to machinery cand amage trees in an obvious way.Hence, care should be taken while the work is in progress. Through various photographs,
‘The Hitavada’ pointed out that debris of construction material were dropped around trees.Such debris contaminate the soil around trees. According to the Bengaluru-based organisation, contamination of soil through the leakage of chemicals from construction materials such as concrete, fuel and oil should be avoided through secure storage. Storage of these must not be near/in the protected zone. Installing irrigation systems androot-tilling planting bed sare two ways the root systems of trees can be damaged. Also, small increases in grade (as little as 2 to 6 inches) that place additional soil over the roots can be devastating for the trees. Damages caused to trees due to devpt activities THE processes involved with construction can be deadly to nearby trees.
These processes may cause physical injury to trunk and crown, cutting of roots, soil compaction, smothering of roots by adding soil, and impact by machinery, contamination of soil. Specified vegetation on ground must be preserved and not trampled upon or choked by construction materials.